Google Patent Describes How Search Queries And Websites Are Classified
- 9 March, 2020
- Jason Ferry
- SEO

Bill Slawski wrote about a Google patent that appears to describe what occurred in the poorly named Medic update. It was stated that the scope is broader than just medical websites. This patent might shed some light as to why some websites cannot rank. Now what should SEO professionals know more about this?
Warning About Patents
It is essential to keep in mind that Google doesn't usually verify whether an algorithm discussed in a patent is in utilisation. This particular patent may or may not be utilised in Google's algorithm.
The Google Patent
The patent discusses a method to categorise sites and search queries by topic.
- Sites are categorised by topics.
- Search queries are categorised by topics.
Knowledge Domains = Topics
In this Google patent, the algorithm is dealing with what it considers as Knowledge Domains that stand for topics. Web pages and search queries can be said to belong to certain knowledge domains.
Knowledge domains described by Bill:
“The words “knowledge domain” stands for topics that a query may be about, and is not a reference to a knowledge graph.”
This is what he said in his article:
“Queries from specific knowledge domains (covering specific topics) might return results using sites that are classified as being from the same Knowledge Domain.”
Topic Pages
A method to simplify this particular idea is to come up with topic buckets. In the topic bucket pages about medical details go in a specific bucket, web pages regarding natural health go into a different bucket, pages about mobile phone reviews into another bucket and pages regarding personal injury lawyers in a certain community may go into the other bucket and so on.
Topic Queries
Based on this patent, queries can likewise be acknowledged as belonging to their very own buckets too. When a user searches for "what is diabetes", Google recognises this particular query as a question about the medical field rather than a query about natural healing.

Google Patent Explains How Queries and Sites Are Classified
This is how the patent describes the classification system:
Classifies queries
“The search engine… may use a classification for a search query to select a category of websites with the same, or a similar, classification.
The search engine… may determine search results from the selected category of websites.”
Classifies sites
“The search engine… may use data from a website classification system… to generate search results. For instance, the website classification system… may generate representations for each of multiple websites… and use the representations to determine a classification for each of the multiple websites…”
Sites Arranged into Clusters
The patent discusses a procedure that arranges the sites by classifying them.
“…the systems and methods described in this document may improve search results pages generated by a search system by including identification of only websites with a particular classification…”
This classification system could produce clusters depending on the likelihood from which a site will have the solution to a search query:
“The website classification system… may determine the classifications based on a likely responsiveness for the websites in the corresponding cluster.
For example, the websites in the first cluster may have a higher likelihood of being responsive to queries in the particular knowledge domain than websites in the second cluster.”
Then it discusses situations where a website may be skipped without getting classified.
What’s fascinating is that it points out skipping analysis as the cluster that a website is in is distant from recognised clusters of websites about a topic.
“In some implementations, one or more of the websites used during training may not be assigned to a classification.
For instance, when a website representation is more than a threshold distance from a cluster, or is otherwise not included in a cluster, the website classification system… may determine to skip using the website representation to create a composite representation, e.g., may determine to skip further analysis for the website during training.”
Authoritativeness is a Classification
“…each website in the plurality of websites may have a score. The score may indicate a classification of the website, such as an authoritativeness, a responsiveness for a particular knowledge domain, another property of the website, or a combination of two or more of these.”
Patent Is Not Just About Medical Websites
What's vital to know is that the procedures discussed in this specific patent apply to a broader range of niche topics. This is not really a Medical Algorithm. It's much more than a simple patent related to the medical field.
Bill stated:
“The patent focused on more than just medical sites. It categorized by industry with health just being one of those. It later sorted by quality scores.
The patent provided an example specifically for medical sites… But it made it clear that it involves multiple industries.
The queries were classified based on knowledge domains also.”
Takeaway: Implications for Ranking
The part about clustering is interesting since it discusses features such as distances and authoritativeness from other clusters of websites.
Links are one way of measuring authority. And it so happens that there's a lot of research into algorithms which sort sites based on topics. The algorithms select seed websites which represent the top authoritative website in a specific topic classification. Some other websites are then arranged based on their distance from the seed websites.
Such an algorithm employs an identical system where a website that is distant from various other clusters will be rejected and not considered for ranking.
There's no mention of links in the context of utilising them as an authority measurement. However, the similarities between link distance ranking algorithms which categorise websites based on topics and creates clusters of websites according to topics are like a mirror to just how the algorithm does identical clustering with content topics.
It might be reasonable to guess that this strengthens the usual belief (and make it more urgent) that links from relevant pages can potentially boost rankings.
Takeaway: Google Update Recovery
Such insights into Google's algorithm support the recommendations about Google update recovery as a whole and in particular, recovering from the Medic Update.
“The so-called “Medic” update appeared to be clearly about relevance issues, not about author bios or “expertise.””
Possibly a key insight from this patent is the fact that it might be beneficial to consider ranking problems from the viewpoint of relevance. After dealing with websites that have dropped rankings, in case your rankings experienced a catastrophic collapse then that might be connected to something identical to what is explained in this specific Google patent.
If your website dropped a number of positions across the board, then that might be other problems such as relevance or increased competition.
No Sites Are Tainted After A Manual Action According To Google
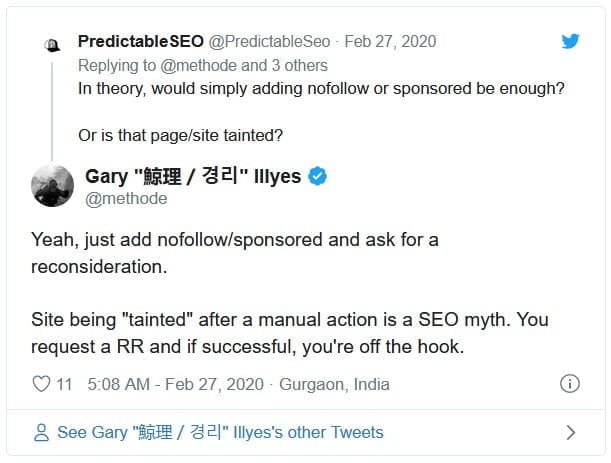
On Twitter, Google’s Gary Illyes stated that a "site being "tainted" after a manual action is a SEO myth." Illyes stated that when you "you request a reconsideration request and if successful, you're off the hook."
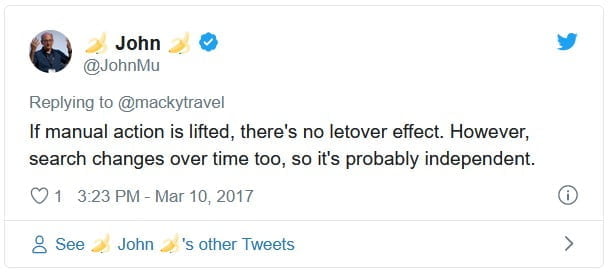
Google has previously mentioned this before so it’s not something entirely new. Google explained that once the manual action is revoked, then there will be no leftover effects. This is what Google stated way back in 2017.
A tweet from Gary in 2020:
A tweet from John in 2017:
However, this does not mean your rankings will bounce back. At times, there could be algorithms that are restraining you even following the removal of a manual action.
Though the particular thing about the website being tainted particularly to that manual action, Google stated that it’s an SEO myth.
Information you read in this SEO UK blog was gathered from https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-algorithm-patent/351146/ and https://ahrefs.com/blog/google-advanced-search-operators.html. Go to these links for further information.
Indeed, working with trustworthy SEO experts is a huge help in improving the quality and ranking of business websites. To know how our services can help you, head over to Position1SEO homepage today.